ASCO GU 2024 Sessions:
![]() DOWNLOAD PDF
DOWNLOAD PDF
RECOMMENDED ABSTRACTS in RENAL CANCERS
 Some Other Text
Some Other Text


These recommended abstracts from ASCO23 Annual meeting have been selected by Robert A. Figlin, MD, Editor-in- Chief of the Kidney Cancer Journal. The chosen abstracts provided here highlight some of the most important trends in ongoing trials and reflect the foremost research and strategies from latest clinical trials that impact the current standard of care in renal cancer.





ABSTRACT LBA358
- Adjuvant nivolumab monotherapy vs placebo for localized renal cell carcinoma at high risk of relapse after nephrectomy: Results from Part B of the randomized, phase 3 CheckMate 914 trial.. Robert J Motzer et alBACKGROUND: CheckMate 914 (NCT03138512) is a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, 2-part trial evaluating adjuvant NIVO plus ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) vs PBO (Part A) or adjuvant NIVO monotherapy vs PBO (and NIVO monotherapy vs NIVO+IPI to assess the contribution of components; Part B) designed in sequence in mutually exclusive patients (pts) with localized RCC at high risk of post-nephrectomy relapse. Results from Part A at 37.0 months median study follow-up (range, 15.4– 58.0) showed no disease-free survival (DFS) benefit for adjuvant NIVO+IPI vs PBO in the overall study population (Lancet 2023;401:821–832). We report primary analyses for Part B of the trial. METHODS: Pts eligible for CheckMate 914 included those undergoing radical or partial nephrectomy between 4 and 12 weeks before randomization with negative surgical margins; with predominantly clear cell histology (with or without sarcomatoid features); pathological TNM stage T2a (grade [G] 3/4) N0M0, T2b-T4 (any G) N0M0, or any T (any G) N1M0; and no evidence of residual disease or distant metastases (M0). Pts in Part B were randomized 2:1:1 to NIVO (240 mg every 2 weeks × 12) plus IPI PBO, NIVO (240 mg every 2 weeks × 12) plus IPI (1 mg/kg every 6 weeks × 4), or matching PBO, and stratified by pathological TNM stage and type of nephrectomy. Treatment was planned for 24 weeks (approximately 5.5 months) or until disease recurrence/unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint for Part B is DFS per blinded independent central review (BICR) for NIVO monotherapy vs PBO. Secondary endpoints include safety of NIVO monotherapy. RESULTS: In total,619 pts were randomized to NIVO monotherapy (n = 411) or PBO (n = 208). With 27.0 months median study follow-up (range, 18.0–42.4), the primary efficacy endpoint of DFS per BICR with NIVO monotherapy vs PBO was not met (hazard ratio [HR], 0.87; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.62– 1.21; P = 0.3962). Median DFS was not reached in either arm; DFS probabilities were 83.3% vs 78.2% (at 12 months) and 78.4% vs 75.4% (at 18 months), respectively. The HR for DFS per investigator was 0.80 (95% CI, 0.58–1.12; P = 0.1936). Median (Q1, Q3) treatment duration was 5.1 (5.1, 5.3) months with NIVO monotherapy and 5.1 (5.1, 5.2) months with PBO. Any-grade treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were reported in 72.5% vs 51.7% of pts treated with NIVO monotherapy (n = 408) vs PBO (n = 207), and grade 3–4 treatment-related AEs were reported in 8.8% vs 1.9%, respectively. Any-grade treatment-related AEs led to discontinuation in 9.6% and 1.0% of pts in the NIVO monotherapy and PBO arms, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: Part B of the CheckMate 914 trial of NIVO monotherapy vs PBO in pts with localized RCC at high risk of relapse after nephrectomy did not meet the primary endpoint of DFS. Safety of NIVO monotherapy was consistent with its known profile in advanced RCC. Clinical trial information: NCT03138512.
ABSTRACT LBA359
Overall survival results from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-564 study of adjuvant pembrolizumab versus placebo for the treatment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Toni Choueiri et alBACKGROUND: The randomized, multicenter, double-blind, phase 3 KEYNOTE-564 study (NCT03142334) showed that adjuvant pembrolizumab improved disease-free survival (DFS) compared with placebo following nephrectomy in participants (pts) with ccRCC at an increased risk of recurrence. We report results from the third prespecified interim analysis with a median follow-up of ~57 months. METHODS: ts were aged ≥18 years and had histologically confirmed ccRCC with or without sarcomatoid features, increased risk of recurrence, ECOG PS of 0 or 1, nephrectomy and/or metastasectomy ≤12 weeks before randomization, and no prior systemic therapy for RCC. Pts were randomly allocated 1:1 to receive pembrolizumab 200 mg or placebo intravenously every 3 weeks for ≥17 cycles (~1 year) or until disease recurrence, intolerable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent. DFS by investigator assessment was the primary end point. Overall survival (OS) was a key secondary end point. Safety was a secondary end point. RESULTS: 994 pts were randomized 1:1 to pembrolizumab (n=496) or placebo (n=498). The median time from randomization to data cut-off date of September 15, 2023, was 57.2 months (range, 47.9−74.5). Statistically significant improvement in OS was observed with pembrolizumab vs placebo (medians not reached, HR 0.62, 95% CI 0.44−0.87; P=.0024). A total of 55 OS events were observed in the pembrolizumab arm and 86 in the placebo arm. The estimated OS rate at 48 months was 91.2% with pembrolizumab and 86.0% with placebo. OS benefit was observed across key subgroups, including in patients with M0 disease (HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.44−0.90) or M1 NED (HR 0.51, 95% CI 0.15−1.75), with PDL1 CPS <1 (HR 0.65, 95% CI 0.31−1.38) or CPS ≥1 (HR 0.62, 95% CI 0.42−0.91), and with presence (HR 0.69, 95% CI 0.28−1.70) or absence (HR 0.57, 95% CI 0.39−0.84) of sarcomatoid features. The observed DFS benefit with pembrolizumab vs placebo was consistent with prior interim analyses (HR 0.72; 95% CI 0.59−0.87). No new safety signals were observed. CONCLUSIONS: After a median of ~57 months of follow-up, adjuvant pembrolizumab demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival versus placebo in participants with RCC at increased risk of recurrence post surgery. KEYNOTE-564 is the first phase 3 study to show improved survival with any adjuvant therapy in RCC. These results continue to support adjuvant pembrolizumab as a standard of
ABSTRACT LBA360
- Subcutaneous nivolumab (NIVO SC) vs intravenous nivolumab (NIVO IV) in patients with previously treated advanced or metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC): Pharmacokinetics (PK), efficacy, and safety results from CheckMate 67T. Saby George et al.
BACKGROUND: NIVO IV has improved outcomes in multiple tumor types. Evolving treatment paradigms have created a need for administration options that address treatment burden and improve efficiencies of healthcare systems. SC delivery of antibodies for various cancer indications has proved safe and effective. CheckMate 67T (NCT04810078) is a multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase 3 study that evaluated PK and objective response rate (ORR) noninferiority of NIVO SC vs IV in patients (pts) with locally advanced or metastatic ccRCC. METHODS: Enrolled pts had measurable disease that progressed during or after 1–2 prior systemic regimens, no prior immuno-oncology treatment, and a Karnofsky performance score ≥ 70. Pts were randomized 1:1 to receive NIVO SC 1200 mg + recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20 Q4W or NIVO IV 3 mg/kg Q2W until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, withdrawal of consent, completion of 2 years’ treatment, or death. The coprimary PK endpoints for noninferiority testing were time-averaged serum concentration over the first 28 days (Cavgd28) and minimum serum concentration at steady state (Cminss) determined by a population PK analysis. ORR by blinded independent central review (BICR) was a key powered secondary endpoint for noninferiority testing. Other secondary objectives included additional PK exposure measures, safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity. RESULTS: A total of 495 pts were randomized to NIVO SC (n = 248) or NIVO IV (n = 247). The median age was 64/66 years in the SC/IV arms. Most pts were male. Average injection time with NIVO SC was < 5 minutes. Noninferiority for the co-primary PK and key powered secondary ORR endpoints was met (see table). Incidence of NIVO SC local injectionsite reactions was 8.1%; reactions were low grade and transient. Most deaths were due to disease progression; study drug toxicity led to 3/1 deaths with NIVO SC/IV. CONCLUSIONS: The co-primary PK and key powered secondary ORR endpoints were met, supporting the use of NIVO SC as a new option to improve healthcare efficiency. The safety profile for NIVO SC was consistent with NIVO IV. Clinical trial information: NCT04810078.
ABSTRACT TPS 496
- - Phase 1b/2 study of combination 177Lu girentuximab plus cabozantinib and nivolumab in treatment naive patients with advanced clear cell RCC.Ghatalia P et al./i>
BACKGROUND: Complete response (CR) is still a rare event in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). The combination of nivolumab plus cabozantinib was recently approved for the firstline treatment of ccRCC based on the CheckMate 9ER phase 3 study demonstrating improved progressionfree survival (PFS) & objective response rate (ORR) in comparison to sunitinib. However, the CR rate was only 9%. Since the anti-tumor effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors are dependent on the presence of activated tumor-infiltrating T cells, drugs that could synergize with T cells' anti-tumor activity can allow us to improve CR rates. Activation of the cGAS-STING pathway which is induced by radiation-induced DNA damage, is one promising mechanism that has been investigated. Many studies have shown that radiation treatment augments immune checkpoint inhibition. However, it is not always possible to radiate all metastatic lesions. Therefore, targeted peptide receptor radionuclide therapies have been developed by conjugating radioisotopes to receptor binding analogs targeting specific cancer cell surface proteins, thereby delivering targeted radiation to cancer cells in the body with minimal damage to surrounding healthy cells. 177Lu girentuximab is the first antibody-radioisotope designed for ccRCC, targeting carbonic anhydrase 9-expressing cells, which includes > 90% of ccRCC. It has been tested in metastatic ccRCC as a single agent & shown to be safe and effective in stabilizing disease in 57% of pts. In this study, we hypothesize 177Lu girentuximab-induced DNA damage will potentiate the STING pathway, and this activation will synergize with nivolumab and cabozantinib to promote trafficking and infiltration of activated T cells to tumors and achieve higher CR rates. METHODS: Up to 100 patients with treatment na'i"ve, biopsy-proven ccRCC with adequate organ/ marrow function with 1 evaluable lesion by RECIST 1.1 will be enrolled. A 5-patient safety lead-in will evaluate myelosuppression. Ongoing safety, & futility monitoring will employ a Bayesian approach. The sample size was chosen for reasonable operating characteristics to distinguish a CR rate (primary endpoint) of 18% as better than 9% using a beta(0.09, 0.91) prior. Secondary endpoints are ORR, PFS by RECIST 1.1, and overall survival. 177Lu-girentuximab 1480 MBq/m2 (61% of single agent MTD) will be administered every 12 weeks for up to 3 cycles. Starting with the 2nd cycle, nivolumab & cabozantinib will be added at standard dose. To explore the effects of the treatment on inducing activated T cell infiltration, patients will undergo pre/post-treatment PET scan with [18F]F-AraG radiotracer as well as biopsies for single cell, spatial transcriptomics and proteomics studies. Clinical trial information: NCT05239533
ABSTRACT TPS 496
- - Phase 1b/2 study of combination 177Lu girentuximab plus cabozantinib and nivolumab in treatment naive patients with advanced clear cell RCC.Barragan-Carrillo R et al.
BACKGROUND: Complete response (CR) is still a
rare event in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell
carcinoma (ccRCC). The combination of nivolumab
plus cabozantinib was recently approved for the firstline
treatment of ccRCC based on the CheckMate 9ER
phase 3 study demonstrating improved progressionfree
survival (PFS) & objective response rate (ORR)
in comparison to sunitinib. However, the CR rate
was only 9%. Since the anti-tumor effects of immune
checkpoint inhibitors are dependent on the presence
of activated tumor-infiltrating T cells, drugs that could
synergize with T cells' anti-tumor activity can allow us
to improve CR rates. Activation of the cGAS-STING
pathway which is induced by radiation-induced DNA
damage, is one promising mechanism that has been
investigated. Many studies have shown that radiation
treatment augments immune checkpoint inhibition.
However, it is not always possible to radiate all
metastatic lesions. Therefore, targeted peptide receptor
radionuclide therapies have been developed by
conjugating radioisotopes to receptor binding analogs
targeting specific cancer cell surface proteins, thereby
delivering targeted radiation to cancer cells in the body
with minimal damage to surrounding healthy cells.
177Lu girentuximab is the first antibody-radioisotope
designed for ccRCC, targeting carbonic anhydrase
9-expressing cells, which includes > 90% of ccRCC.
It has been tested in metastatic ccRCC as a single
agent & shown to be safe and effective in stabilizing
disease in 57% of pts. In this study, we hypothesize
177Lu girentuximab-induced DNA damage will
potentiate the STING pathway, and this activation
will synergize with nivolumab and cabozantinib to
promote trafficking and infiltration of activated T cells
to tumors and achieve higher CR rates.
METHODS: Up to 100 patients with treatment
na'i"ve, biopsy-proven ccRCC with adequate organ/
marrow function with 1 evaluable lesion by RECIST
1.1 will be enrolled. A 5-patient safety lead-in will
evaluate myelosuppression. Ongoing safety, & futility
monitoring will employ a Bayesian approach. The
sample size was chosen for reasonable operating
characteristics to distinguish a CR rate (primary
endpoint) of 18% as better than 9% using a beta(0.09,
0.91) prior. Secondary endpoints are ORR, PFS by
RECIST 1.1, and overall survival. 177Lu-girentuximab
1480 MBq/m2 (61% of single agent MTD) will be
administered every 12 weeks for up to 3 cycles. Starting
with the 2nd cycle, nivolumab & cabozantinib will be
added at standard dose. To explore the effects of the
treatment on inducing activated T cell infiltration,
patients will undergo pre/post-treatment PET scan
with [18F]F-AraG radiotracer as well as biopsies for
single cell, spatial transcriptomics and proteomics
studies. Clinical trial information: NCT05239533
ABSTRACT 361
- - Belzutifan versus everolimus in participants (pts) with previously treated advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC): Patient-reported outcomes in the phase 3 LITESPARK-005 study.Thomas Powles et al.
BACKGROUND: In the randomized, open-label,
phase 3 LITESPARK-005 (NCT04195750) study,
belzutifan treatment showed superior PFS (primary
endpoint; HR 0.75 [95% CI 0.63–0.90]; P<.001) and
ORR (key secondary endpoint; estimated percentagepoint
difference 18.4 [95% CI 14.0–23.2]; P<.00001) vs
everolimus in pts with advanced/metastatic clear cell
RCC that progressed after prior immune checkpoint
and anti-angiogenic therapies. We present PRO findings
for belzutifan vs everolimus in LITESPARK-005.
METHODS: PROs were evaluated by FKSI-DRS and
EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaires in all randomized
pts with ≥1 dose study treatment and ≥1 completed
PROs assessment, administered electronically on d
1 of wk 1, 3, 5, and 9, Q4W thereafter, at treatment
discontinuation, and d 30 after last dose. Time to
deterioration (TTD) and least square (LS) mean
change from baseline as measured by FKSI-DRS and
QLQ-C30 global health status/quality of life (GHS/
QoL) and physical functioning (PF) scales were
prespecified as secondary endpoints. PROs were not
formally statistically tested and 95% CI and P-values
were nominal and descriptive.
RESULTS: As of June 13, 2023 (data cutoff date at
second prespecified interim analysis), median (range)
follow-up was 25.7 mo (16.8–39.1). Median (range)
duration of treatment was 7.6 mo (0.1–35.8) with
belzutifan vs 3.9 mo (0.0–33.2) with everolimus; 84
(22.6%) vs 18 (5.0%) pts remained on treatment. 366
of 374 pts randomized to belzutifan and 354 of 372
pts randomized to everolimus were included in the
PRO analysis population. Completion rates for FKSIDRS
and QLQ-C30 were >90% at baseline and >55%
at wk 17 (~4 mo) in each arm. Meaningfully longer
TTD in FKSI-DRS and QLQ-C30 GHS/QoL scores
were observed for belzutifan vs everolimus (Table).
LS mean changes in FKSI-DRS and QLQ-C30 GHS/
QoL scores suggested stability from baseline to wk
17 with belzutifan vs worsening with everolimus,
and a potential greater worsening in PF scores with
everolimus vs belzutifan.
CONCLUSIONS: Belzutifan was associated with
prolonged TTD in FKSI-DRS and EORTC QLQ-C30.
Score changes from baseline to wk 17 also favored
belzutifan over everolimus. Overall, PRO results
indicate better disease-specific symptoms and quality
of life among pts treated with belzutifan compared with
everolimus. Clinical trial information: NCT04195750
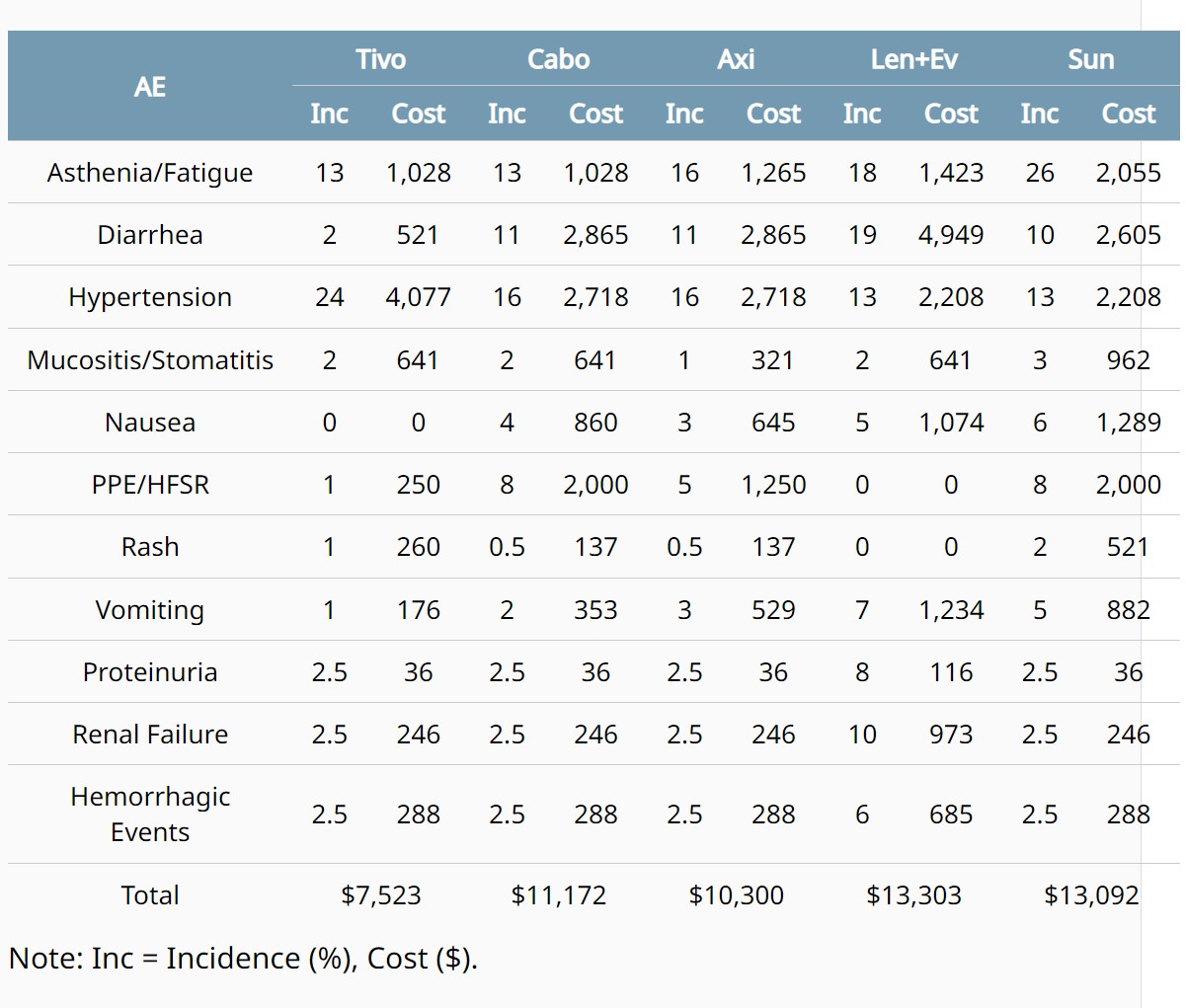
ABSTRACT 363
- Nivolumab plus ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) vs sunitinib (SUN) for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC): Long-term follow-up data from the phase 3 CheckMate 214 trial.Nizar Tannir et al. BACKGROUND: First-line NIVO+IPI has provided substantial long-term survival benefits over SUN in patients (pts) with aRCC in CheckMate 214. We report survival, response per independent radiology review committee (IRRC) and safety after 6 y minimum (80 mo median) follow-up in all randomized pts, by IMDC risk and in pts with overall survival (OS) ≥ 6 y (long-term survivors; LTS). Longer follow-up data (minimum, 7.5 y) will be presented.
METHODS:
Pts with clear cell aRCC were randomized 1:1 to
NIVO 3 mg/kg + IPI 1 mg/kg Q3W×4 then NIVO
3 mg/kg Q2W vs SUN 50 mg QD for 4 wk on, 2 wk
off. Endpoints: OS, progression-free survival (PFS)
and objective response rate (ORR; both per IRRC
using RECIST v1.1) in IMDC intermediate/poor risk
(IP; primary), intent-to-treat (ITT; secondary) and
favorable risk (FAV; exploratory) pts. Exploratory
outcomes in LTS pts were assessed post hoc.
RESULTS: OS with NIVO+IPI vs SUN remained
superior in ITT (HR 0.72) and IP (HR 0.68) pts; OS
benefits were similar between arms in FAV pts (HR
0.87; Table). Median PFS was consistent with previous
reports. ORR per IRRC was higher with NIVO+IPI
vs SUN, with more ongoing responses in ITT (60% vs
50%) and IP (60% vs 50%) pts. In FAV pts, ORR was
lower with NIVO+IPI vs SUN, yet more responses
were ongoing (59% vs 52%, respectively). Median
duration of response (DOR) was longer and complete
response (CR) rate was higher with NIVO+IPI vs
SUN regardless of IMDC risk. Incidence of any and
grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse events remained
largely unchanged. One additional drug-related death
occurred with NIVO+IPI and zero with SUN since
the previous database lock. In the LTS subgroup
(NIVO+IPI, n = 208; SUN, n = 151), ORR was higher
(66% vs 53%), more pts had a CR (27% vs 9%) and
fewer progressed (4% vs 11%) with NIVO+IPI vs SUN.
Median DOR was longer with NIVO+IPI (n = 137) vs
SUN (n = 80) among LTS with confirmed response (76
vs 40 mo). Updated survival, response and safety data
with 7.5 y minimum follow-up, along with additional
subgroup analyses, will be presented.
CONCLUSIONS: NIVO+IPI demonstrated long-term
survival and more durable response benefits vs SUN
in ITT and IP pts. CR rates were higher and median
DOR was longer with NIVO+IPI vs SUN regardless of
IMDC risk group, and in LTS pts. No new safety signals
emerged. Clinical trial information: NCT02231749.

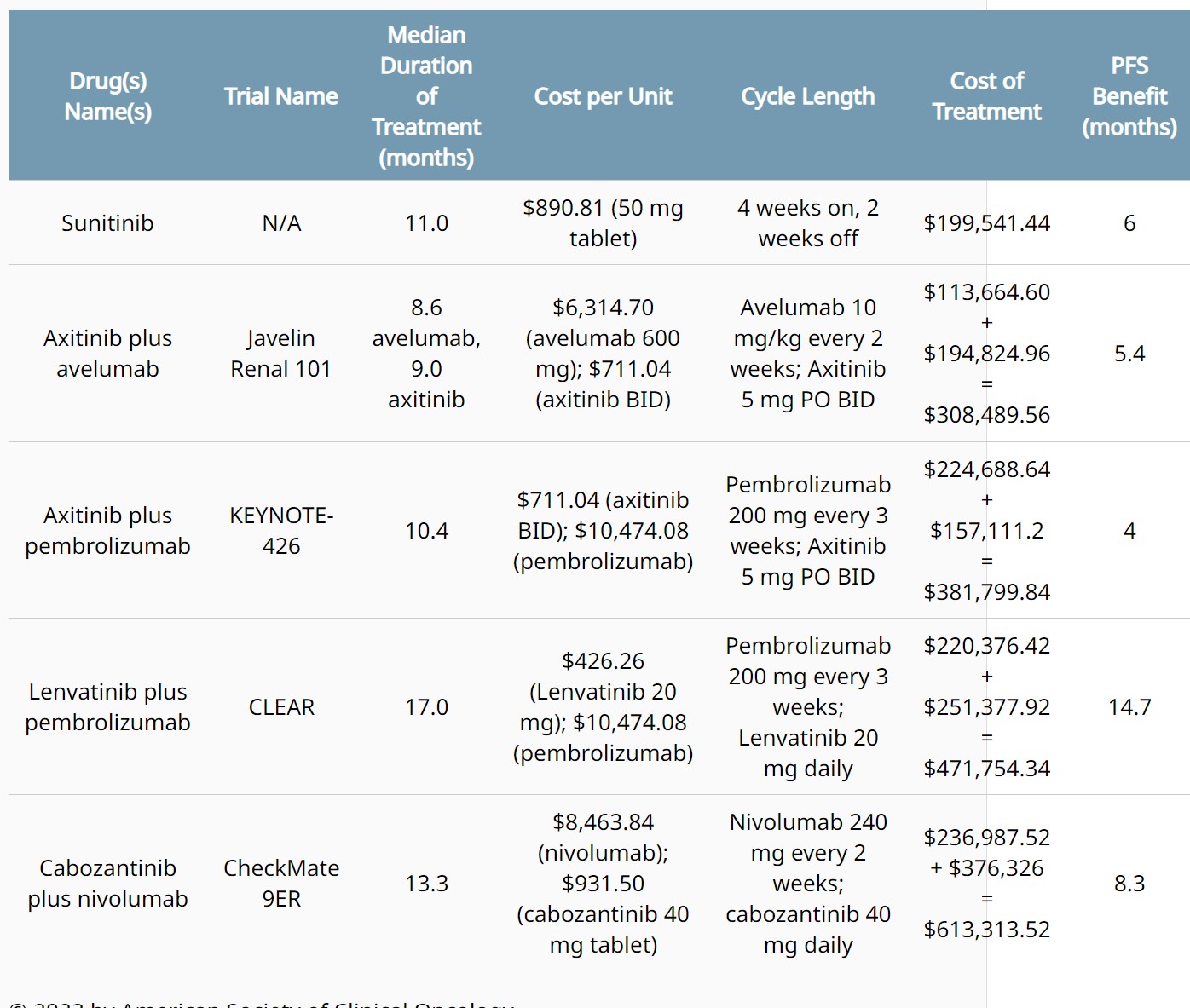

ABSTRACT 364
- - Subgroup analyses of efficacy outcomes by baseline tumor size in the phase 3, openlabel CLEAR trial.Viktor Grünwald et al.
BACKGROUND: In the primary analysis of the phase 3 open-label CLEAR trial, lenvatinib + pembrolizumab (L+P) showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and objective response rate (ORR) compared with sunitinib (S) in patients (pts) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC) (Motzer NEJM 2021). Outcomes were further corroborated by results of the final prespecified analysis of CLEAR (Motzer ASCO 2023). We report efficacy outcomes per baseline tumor size in the L+P arm of CLEAR. METHODS: 1069 treatment-naïve pts with aRCC and a clear-cell component were randomized (1:1:1) to: L 20 mg PO QD + P 200 mg IV Q3W; or L 18 mg + everolimus 5 mg PO QD; or S 50 mg PO QD (4 wks on/2 wks off). Stratification factors included geographic region and MSKCC prognostic risk group. IMDC risk groups (derived programmatically) are presented in this analysis. Efficacy outcomes were evaluated by quartiles of baseline sums of diameters of target lesions. Tumor assessments were performed by independent imaging review per RECIST v1.1. RESULTS: Pts were grouped into 4 categories: ≤Q1 (34.72 mm), >Q1 - ≤Q2 (60.06 mm), >Q2 - ≤Q3 (108.56 mm) and >Q3 per baseline tumor sizes (Table). For pts with ≤Q1 baseline tumor sizes, 40.7% and 58.0% were in the favorable and intermediate + poor IMDC risk subgroups, respectively. For pts with >Q3 baseline tumor sizes, 6.3% and 93.8% were in the favorable and intermediate + poor IMDC risk groups, respectively. Median OS, PFS, ORR, complete response (CR), partial response (PR), and near-CR (PR with maximum tumor shrinkage ≥75%) by baseline tumor size categories are in the Table. CONCLUSIONS: In CLEAR, clinically meaningful efficacy with L+P was observed across pts with aRCC irrespective of their baseline tumor sizes. These results support the use of L+P for the 1L treatment of aRCC across pts with both low and high baseline tumor size. Clinical trial information: NCT02811861.
ABSTRACT 365
- - Development of a patientcentered health-related quality of life (HRQOL) measure for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC): A three-phase studya...Voss MH et al.
BACKGROUND:Patients(pts)with mRCC require a tailored HRQOL assessment. Previous research (Bergerot et al. Oncologist 2023; Bergerot et al. J Clin Oncol 2023) explored FKSI-19, EORTC QLQ-C30, and EQ-5D item relevance. We aimed to develop a tailored HRQOL measure for pts with mRCC through a three-phase approach involving patient engagement, expert input, and advocacy. METHODS: In Phase 1, 117 pts with mRCC (83:34 M:F, median age=64) from the US, Europe and Brazil participated in a survey study to assess the relevance of items from established measures (FKSI-19, EORTC QLQ-C30, EQ-5D). In this cohort, 88% of pts had clear cell histology received immunotherapy alone, targeted therapy alone or combination therapy, respectively. Questions identified as relevant (base on $66%consensus) were selected for inclusion in a preliminary survey. Phase 2 involved assembling a panel of 11 experts who rigorously reviewed and refined survey questions. In Phase 3, preliminary version were presented to 8 patient advocates (5:3 F:M; 6:2 pts:caregivers) to ensure alignment with pts’ needs and experiences. Results: Phase 1 analysis identified 10 items. Pts requested the inclusion of a question about social/family issues and better coverage of emotional symptoms. An 12-item questionnaire was created, and the expert committee refined three items to incorporate patient suggestions and added one item related to functional status (Table). This questionnaire included 1 cancer-specific item, 3 cancer or treatmentspecific items, 3 nonspecific emotional items, and 4 non-specific physical items. Patient advocates provided feedback, agreeing with the items excluded from previous questionnaires and those included. They suggested minor edits to item wording. CONCLUSIONS: The novel approach holds the potential to replace traditional HRQOL measures that may lack relevance to specific clinical circumstances. Further validation is planned in a phase 3 trial, ensuring its applicability in clinical practice.
ABSTRACT 373
- - First-in-human safety, imaging and dosimetry of [68Ga]Ga-DPI-4452, a novel CA IX-targeting peptide, in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma..Michael S Hofman et al.
BACKGROUND:
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) is overexpressed in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and is associated
with aggressive tumor behavior, treatment resistance
and overall poor outcomes. DPI-4452 is a first-in-class,
cyclic peptide that binds with high affinity to CA IX.
Radiolabeling DPI-4452 with gallium-68 ([68Ga]Ga-
DPI-4452) or lutetium-177 ([177Lu]Lu-DPI-4452) is
an innovative, theranostic approach for identifying
and treating patients with CA IX-expressing tumors.
Compared with existing antibody approaches, a
radiolabeled peptide may confer better characteristics
for both PET-CT imaging and therapy. This firstin-
human study (NCT05706129) is evaluating the
theranostic potential of [68Ga]Ga-DPI-4452 and
[177Lu]Lu-DPI-4452 in patients with unresectable
metastatic ccRCC, colorectal cancer or pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma tumors. Here we report safety,
tolerability, pharmacokinetics, dosimetry and imaging
characteristics of [68Ga]Ga-DPI-4452 from the
completed ccRCC imaging cohort.
METHODS: 1The DPI-4452 peptide contains a DOTA
cage and is radiolabelled with [68Ga]Ga. Following
intravenous injection of [68Ga]Ga-DPI-4452,
patients underwent serial PET-CT imaging, urine
and blood sampling to assess imaging characteristics,
biodistribution, and dosimetry of [68Ga]Ga-DPI-4452.
Patients were followed for 7 days post-injection for
safety observations.RESULTS: Pts were grouped into 4
categories: ≤Q1 (34.72 mm), >Q1 - ≤Q2 (60.06 mm),
>Q2 - ≤Q3 (108.56 mm) and >Q3 per baseline tumor
sizes (Table). For pts with ≤Q1 baseline tumor sizes,
40.7% and 58.0% were in the favorable and intermediate
+ poor IMDC risk subgroups, respectively. For pts with
>Q3 baseline tumor sizes, 6.3% and 93.8% were in the
favorable and intermediate + poor IMDC risk groups,
respectively. Median OS, PFS, ORR, complete response
(CR), partial response (PR), and near-CR (PR with
maximum tumor shrinkage ≥75%) by baseline tumor
size categories are in the Table.
RESULTS: A mean activity of 185 MBq [68Ga]Ga-
DPI-4452 was administered to 3 patients with ccRCC.
No clinically significant toxicities were observed. PETCT
images showed rapid and sustained tumor uptake
over 4 h, as well as rapid renal elimination. At 1 h, the
maximum tumor standardized uptake value (SUVmax)
across 36 lesions ranged from 6.8 to 211.6, with a mean
of 64.6. Seventeen of these lesions (found in lymph
nodes, lung, pancreas, parotid gland and other sites)
were not detectable on prior contrast-enhanced CT.
OLINDA dosimetry estimates revealed that the organs
receiving the highest absorbed doses (mean [SD] mGy/
MBq) were stomach wall (0.33 [0.10]), small intestine
wall (0.33 [0.08]) and gallbladder wall (0.21 [0.12]),
with a mean whole body effective dose of 0.06 [0.02]
mSv/MBq. Absorbed doses in the kidney, liver and
bone marrow were low. Over 80% of total administered
radioactivity cleared from the bloodstream within 1 h.
CONCLUSIONS:
[68Ga]Ga-DPI-4452 provides exceptional images in
patients with ccRCC without clinically significant
toxicity. Very high SUVs and tumor-to-background
ratios suggest potential for use in both diagnostics
and patient selection for therapy. The tumor retention
and rapid elimination support potential of [177Lu]
Lu-DPI-4452 radioligand therapy. Clinical trial
information: NCT05706129.

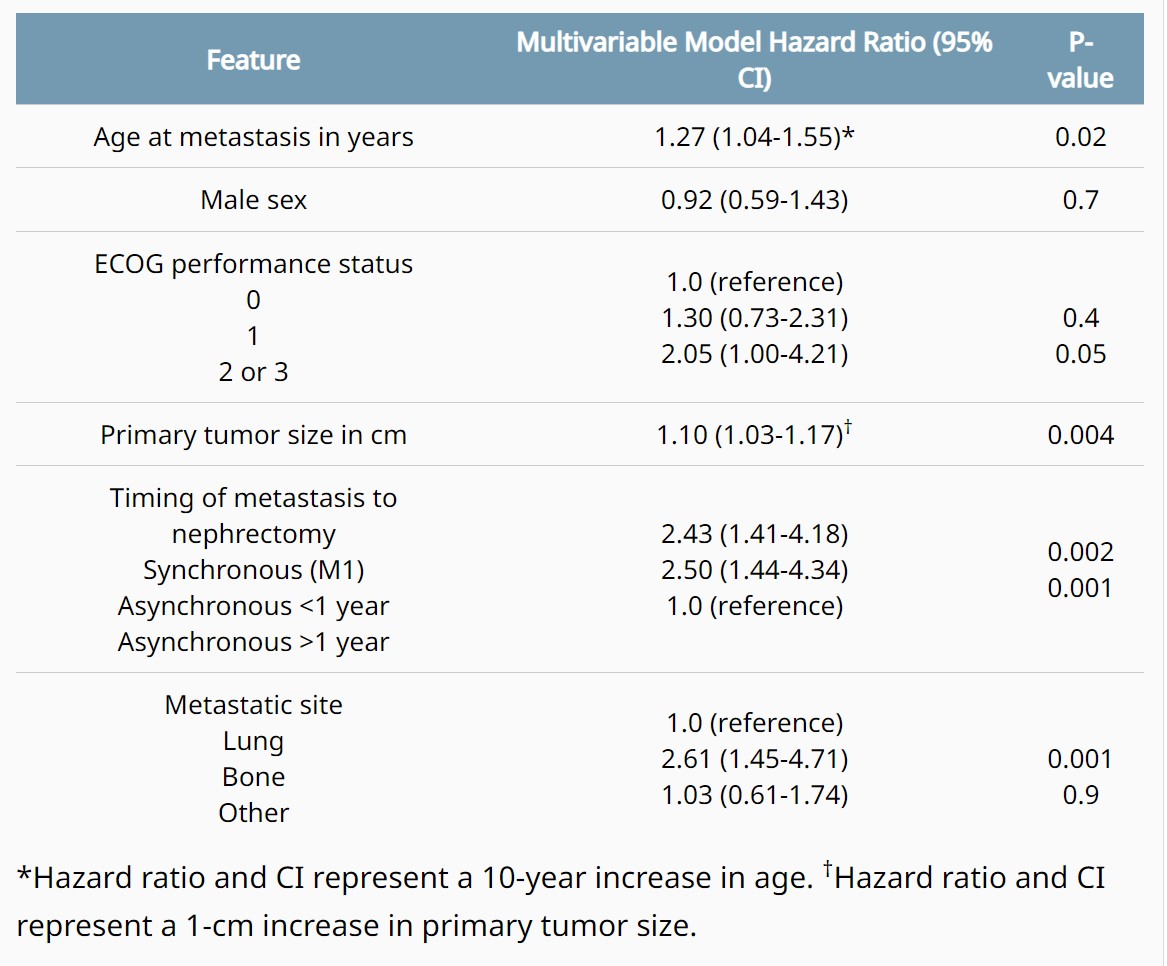

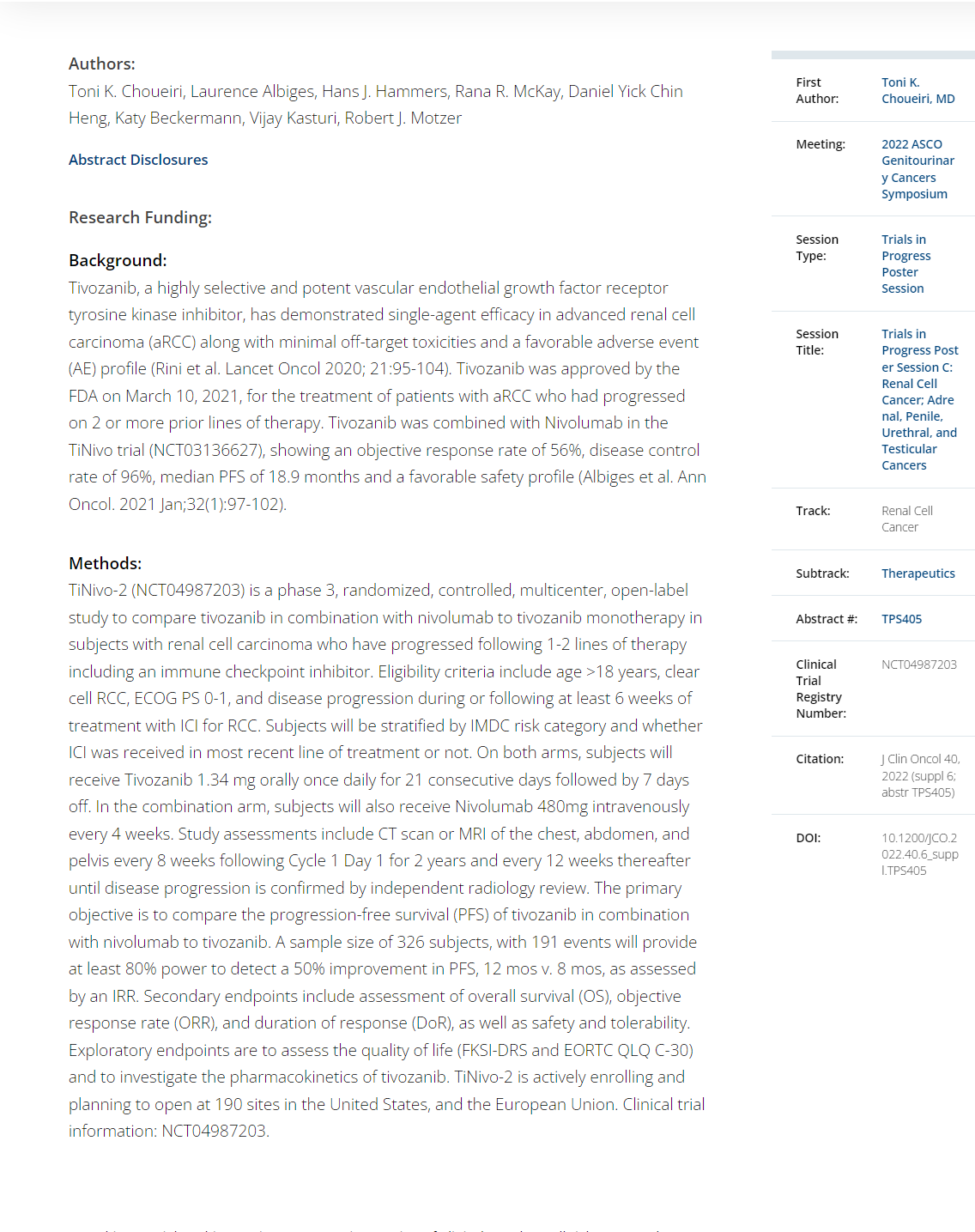
ABSTRACT 684
- - Cabozantinib in combination with atezolizumab in non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Extended follow-up results of cohort 10 of the COSMIC-021 study.Bradley Alexander McGregor et al.
Background: In the COSMIC-021 phase 1b study (NCT03170960) evaluating cabozantinib plus atezolizumab in advanced solid tumors, this combination therapy demonstrated encouraging clinical activity in patients with advanced non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (nccRCC) with a median follow-up of 13 mo (Pal. JCO 2021). Results after extended follow-up in nccRCC are presented. Methods: Patients with advanced nccRCC and ECOG PS 0/1 who had ≤1 prior VEGFR-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) were eligible. Prior treatment with TKIs targeting MET or immune checkpoint inhibitors was not allowed. Patients received cabozantinib 40 mg PO QD plus atezolizumab 1200 mg IV Q3W until unacceptable toxicity or progression; dose reductions of cabozantinib (40 mg QD to 20 mg QD, then to 20 mg QOD) were permitted to manage adverse events. The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR) per RECIST v1.1 by the investigator; other endpoints included safety, duration of response (DOR), PFS, and OS. Results: The study enrolled 32 patients with nccRCC (2 from dose escalation phase, and 30 from expansion phase of the study): median age, 62 y; male, 81%; ECOG PS 0/1, 75%/25%; histology, papillary/chromophobe/clear cell/other, 47%/28%/3%/22%; sarcomatoid feature, 13%; IMDC risk favorable/intermediate/poor, 50%/41%/9%; ≥3 tumor sites, 56%; tumor sites, lung/kidney/bone/liver, 50%/25%/16%/16%; prior nephrectomy, 63%; prior VEGFR TKI, 22%; 0/1 lines of prior therapy (locally advanced/metastatic setting), 81%/19%. As of July 21, 2022, median follow-up was 37.2 mo (range 32.1–58.5) with 5 (16%) patients remaining on study treatment. ORR by investigator was 31% (all PRs) and disease control rate was 94% (Table); median DOR was 8.1 mo. Median PFS was 9.3 mo (95% CI 5.5–12.3), and median OS was not reached (95% CI 23.0–NE). PFS and OS estimates at 12 mo were 34% and 84%, respectively; 24-mo estimates were 6% and 70%. Treatment-related AEs occurred in 97% (grade 3/4, 53%); the most common AEs included diarrhea (69%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (50%), fatigue (44%), dysgeusia (41%), hypertension (31%) and nausea (31%). One grade 5 treatment-related AE of pulmonary hemorrhage occurred. Treatment-related AEs leading to discontinuation of both study treatments occurred in 13% of patients. Conclusions: Extended 3-year follow-up reinforces the encouraging clinical activity of cabozantinib plus atezolizumab in advanced nccRCC with a manageable safety profile. Clinical trial information: NCT03170960.

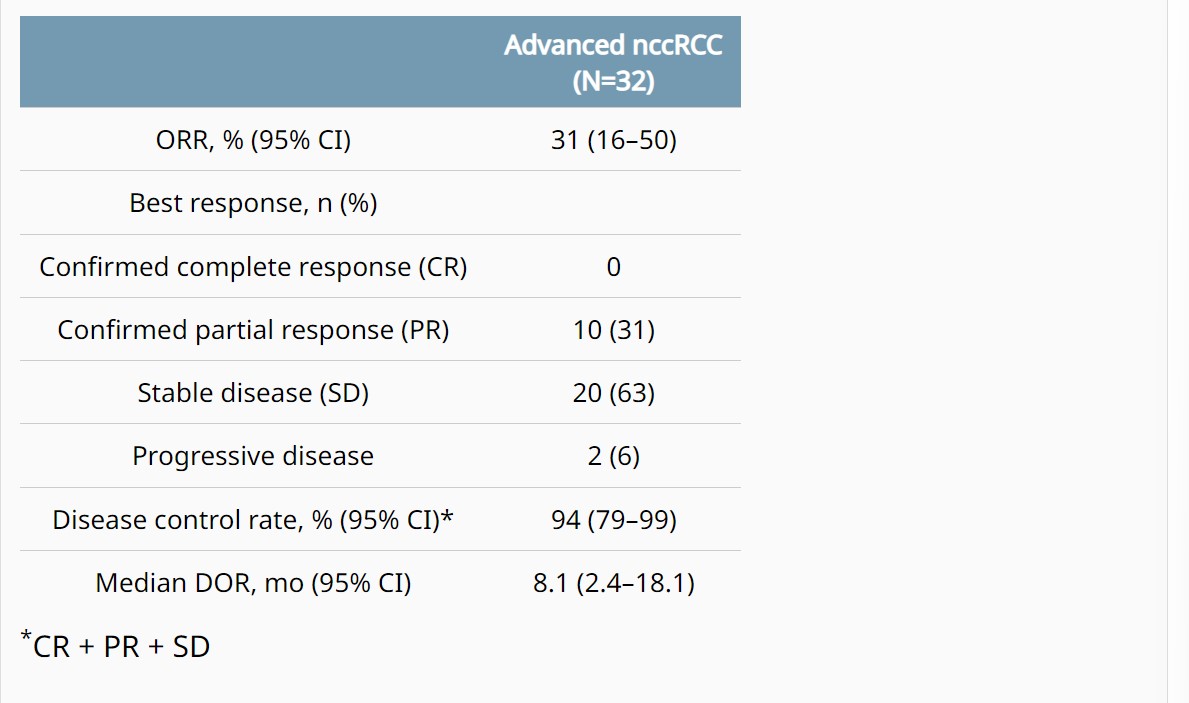

ABSTRACT 714
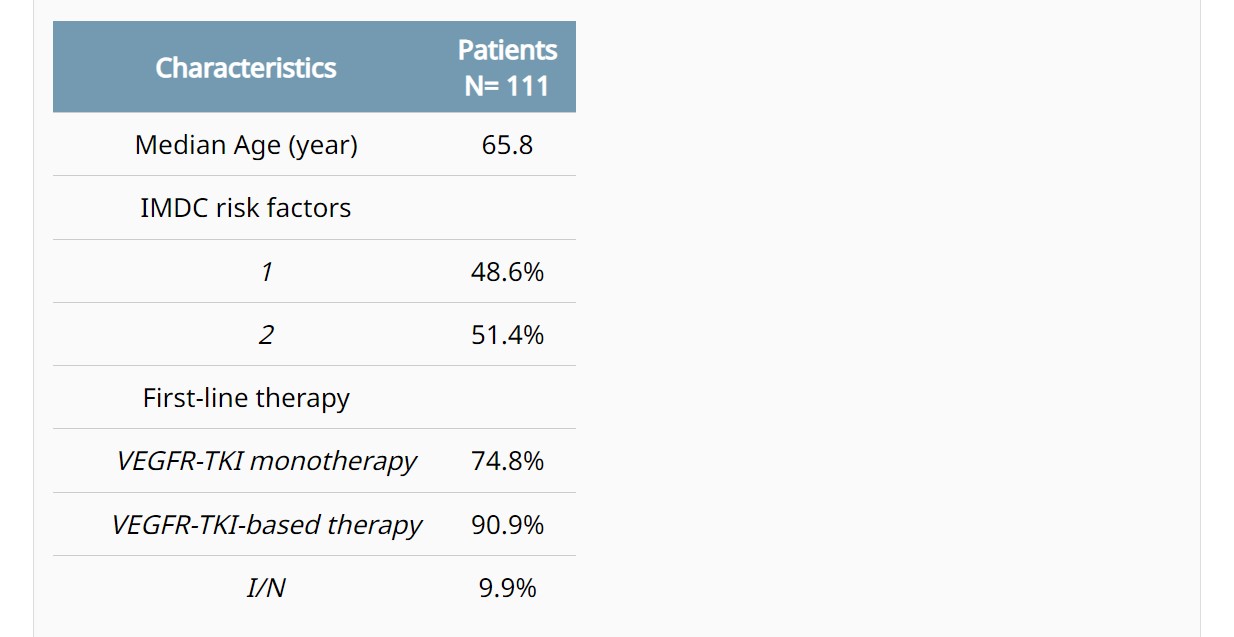
- - Evaluation of PBRM1, PD-L1, CD31, and CD4/CD8 ratio as a predictive signature of response to VEGFR-TKI–based therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) with IMDC intermediate prognosis: Results from the APAChE-I Study.Chiara Ciccarese et al.
Background: Intermediate IMDC group is the largest and most heterogeneous group of mRCC. Current first-line (1L) therapy options for these patients (pts) are based on either an anti-angiogenic agent (VEGFR-TKI) combined with immunotherapy (IO), or a combo of IO (ipilimumab+nivolumab [I/N]). No biomarkers (BM) for selecting the most effective regimen have been identified so far. Methods: Immunohistochemical expression of PBRM1, PD-L1, CD31, and CD4/CD8 ratio was evaluated on histological samples of intermediate-risk mRCC pts treated with VEGFR-TKI monotherapy, and then in pts receiving a VEGFR-TKI-based therapy or the immune doublet I/N. PBRM1 positivity score was based on the percentage of positive cells and on the intensity of nuclear expression; PD-L1 positivity was defined as CPS≥10; CD31 high-density had moderate to strong nuclear staining; and the CD4/CD8 ratio cut-off for positivity was >0.2. Cox model was used to assess the correlation between BM and outcomes; PFS and OS were estimated by Kaplan-Meier method. Results: After screening of tumor tissues from 150 pts, a total of 111 were included in the final analysis (Table). In pts treated with VEGFR-TKI monotherapy, a significant correlation with PFS was observed with loss of PBRM1 expression (HR 0.58, p=0.035), PD-L1 negativity (HR 0.44, p=0.048), and high CD4/CD8 ratio (HR 0.62, p=0.073). CD31 density did not significantly correlate with PFS. A profile potentially predictive of angiogenesis (AP+) was defined based on the PBRM1 loss, PD-L1 negative, and high CD4/CD8. In pts treated with VEGFR-TKI monotherapy, tumors with the AP+ (43% of all cases) had a significantly longer median PFS (mPFS 23.8 vs. 11.8 months, p=0.003) and mOS (41.5 vs. 26.9 months, p=0.024) compared to the others. The AP+ retained its significant correlation with PFS (mPFS 23.8 vs. 11.1 months, p<0.001) and OS (41.5 vs. 24.9, p=0.006) in pts receiving VEGFR-TKI-based therapies. The rate of AP+ tumors was 55.6% and 32.7% in pts with one or two IMDC risk factors, respectively (p=0.022). In the small cohort of pts treated with I/N, no differences were observed in PFS (p=0.64) and OS (p=0.75) between AP+ and AP-negative. Conclusions: The AP+ signature (loss of PBRM1, PD-L1 negative, and CD4/CD8 high ratio) was associated with improved clinical outcomes in mRCC pts at IMDC intermediate prognosis treated with VEGFR-TKI-based therapy; this correlation was significant regardless from the addition of IO to VEGFR-TKI monotherapy. Prospective validation of this signature is required for guiding the selection of the most appropriate 1L therapy.


ABSTRACT TPS747
- -LITESPARK-024: A randomized phase 1/2 study of belzutifan with or without palbociclib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.David F. McDermott, et al.
Background: The combination of immunotherapy with antiangiogenic agents is a well-established first-line treatment option for patients (pts) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), but many pts develop resistance, and effective second- or subsequent-line options are needed. The von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene is inactivated in approximately 90% of RCC cases, which results in the constitutive activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) signaling. HIF-2α is involved in angiogenesis, tumor growth, proliferation, and metastasis, and is a key oncogenic driver in RCC. The HIF-2α inhibitor belzutifan has demonstrated promising antitumor activity with manageable safety in pts with heavily pretreated RCC. The cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) pathway is altered in several cancer types, including RCC, and is associated with poor clinical outcomes. The CDK 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib inhibited cell growth in RCC cell lines, and the antiproliferative effects of CDK 4/6 inhibition were synergistic with HIF-2α inhibition in HIF-2α–dependent VHL -/- clear cell RCC cell lines. We hypothesized palbociclib could potentially enhance the efficacy of belzutifan as combination therapy for previously treated pts with advanced RCC. Methods: LITESPARK-024 (NCT05468697) is an open-label, multicenter, phase 1/2 randomized study of belzutifan + palbociclib versus belzutifan monotherapy in pts with advanced RCC. Pts must have histologically confirmed unresectable stage IV RCC with a clear cell component, received at least 2 prior systemic regimens (both an anti–PD-1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibody and a VEGF receptor–targeted TKI, in sequence or in combination), have measurable disease per RECIST v1.1 by BICR, have KPS score of ≥70%, and have radiographic disease progression on or after the most recent regimen per investigator. Part 1 will evaluate the safety of belzutifan + palbociclib and determine the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) for the combination using a modified toxicity probability interval design. Part 2 will evaluate the safety and efficacy of belzutifan + palbociclib versus belzutifan alone. In part 1, ≤30 pts will be enrolled into 3 dose groups and receive belzutifan 120 mg once daily + palbociclib (75, 100, or 125 mg) daily for 21 consecutive days followed by 7 days off. In part 2, approximately 150 pts will be randomly assigned 2:1 to receive belzutifan 120 mg once daily + palbociclib RP2D (21 consecutive days/7 days off) or belzutifan 120 mg once daily. Pts will be stratified by IMDC risk (0 vs 1-2 vs 3-6) and sarcomatoid histology (yes vs no) at randomization in part 2. The primary end point for part 1 is to assess dose-limiting toxicities and adverse events to determine the RP2D of belzutifan + palbociclib. The primary end point for part 2 is ORR per RECIST v1.1 by investigator assessment. Secondary end points for part 2 are clinical benefit rate, DOR, PFS, OS, and safety and tolerability. Clinical trial information: NCT05468697.
ABSTRACT TPS748
- - Phase 3 LITESPARK-022: Pembrolizumab (pembro) plus hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) inhibitor belzutifan as adjuvant treatment for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).Toni K. Choueiri, et al.
Background: Treatment with the PD-1 inhibitor pembro produced significant improvement in disease-free survival after surgery for patients (pts) with ccRCC in the phase 3 KEYNOTE-564 trial. Based on these results, pembro was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency for adjuvant treatment of pts with RCC at increased risk of recurrence following nephrectomy or following nephrectomy and resection of metastatic lesions. Despite advances in the treatment landscape for RCC, more effective adjuvant treatment strategies are needed for pts at risk of recurrence after surgery. HIF-2α is an established oncogenic driver in ccRCC, and promising antitumor activity in advanced ccRCC and von Hippel-Lindau disease–associated RCC has been demonstrated with the HIF-2α inhibitor belzutifan. The multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 LITESPARK-022 study (NCT05239728) will evaluate the efficacy and safety of pembro plus belzutifan compared with placebo plus pembro as adjuvant treatment following nephrectomy in pts with ccRCC. Methods: Key eligibility criteria include adults with histologically or cytologically confirmed intermediate-high risk, high risk, or M1 with no evidence of disease (NED) RCC with a clear cell component; pts with no prior systemic therapy, nephrectomy, and/or metastasectomy ≤12 weeks before randomization; and pts who are tumor free per computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging. Approximately 1600 pts will be randomly assigned to receive belzutifan 120 mg orally once daily plus pembro 400 mg intravenously (IV) every 6 weeks (Q6W) for ≤9 administrations (~54 weeks) or oral placebo plus pembro 400 mg IV Q6W for ≤9 administrations (~54 weeks) or until verified disease recurrence by blinded independent central review, start of new anticancer treatment, unacceptable toxicity, or decision to withdraw. Stratification factors are tumor grade (1 or 2 vs 3 or 4) and risk type (intermediate-high risk versus high risk versus M1 NED). Pts will be radiologically evaluated Q12W from randomization through year 2, Q16W in years 3 to 5, and Q24W in years 6 and beyond. Adverse events will be monitored throughout the study and for 30 days following cessation of study treatment (90 days for serious adverse events). The primary end point is disease-free survival. Secondary end points include overall survival, safety, disease recurrence–specific survival, and patient-reported outcomes. Recruitment is underway in Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America. © 2022 American Society of Clinical Oncology, Inc. Reused with permission. This abstract was accepted and previously presented at the 2022 ASCO Annual Meeting. All rights reserved. Clinical trial information: NCT05239728.